精神科藥物交互作用
精神科藥物與 GLP-1 受體促效劑交互作用查詢系統
提供 Semaglutide 與 Tirzepatide 與各類精神科藥物的交互作用資訊,協助臨床用藥決策
風險等級說明
交互作用風險分佈
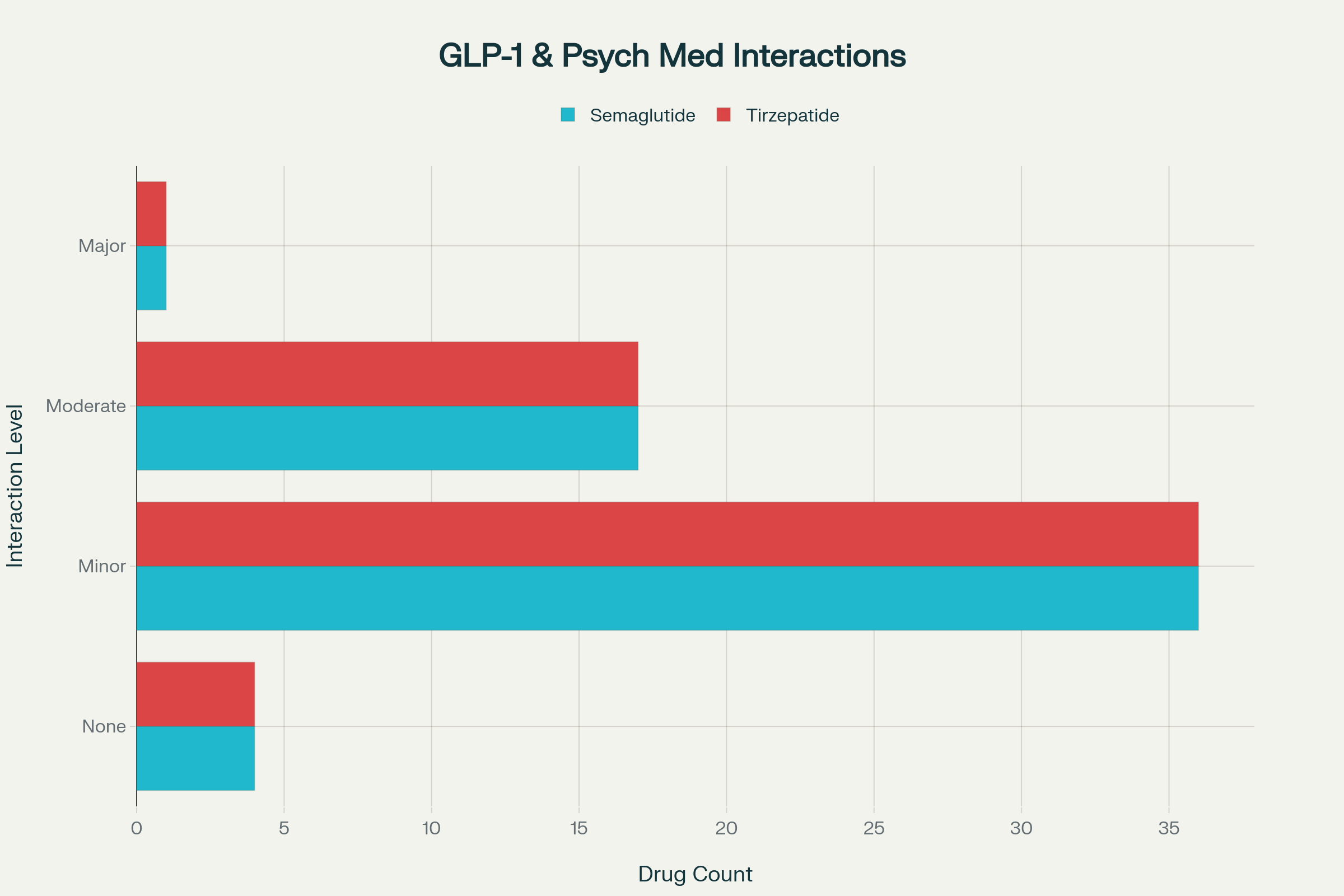
藥物資訊
參考文獻
-
Hejdak D, et al. (2024). Interaction of Semaglutide and Ziprasidone in a Patient With Schizophrenia: A Case Report. Cureus.
主要發現:Semaglutide 延緩胃排空,影響 Ziprasidone 吸收與代謝,導致血中濃度升高。 -
Chen W, et al. (2024). Psychiatric adverse events associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists: analysis of the FAERS database. BMC Pharmacovigilance.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑使用者 4.55% 報告精神科不良反應。 -
Kornelius E, et al. (2024). The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidal behavior in diabetes patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Nature Scientific Reports.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑治療者精神障礙風險上升 98%。 -
Tobaiqy M, et al. (2024). Psychiatric adverse events associated with semaglutide, liraglutide and tirzepatide: analysis of EudraVigilance data. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.
主要發現:最常見精神不良反應為憂鬱 (50.3%)、焦慮 (38.7%)、自殺意念 (19.6%)。 -
Calvarysky B, et al. (2024). Drug-Drug Interactions Between Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Oral Drugs: A Systematic Review. Annals of Pharmacotherapy.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑會延遲胃排空改變口服藥物吸收,但總體藥物暴露量臨床變異性有限。 -
Durell N, et al. (2022). Effect of Antidepressants on Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Weight Loss. Obesity Research.
主要發現:抗憂鬱藥物可能減弱 GLP-1 受體促效劑造成的減重效果。 -
Prasad F, et al. (2023). Semaglutide for the treatment of antipsychotic-associated weight gain: a case series. Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology.
主要發現:Semaglutide 成功降低無法用 Metformin 控制的抗精神病藥相關體重增加。 -
Kido K, et al. (2024). Call to action for drug interactions between tirzepatide and heart failure guideline-directed medical therapy. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association.
主要發現:Tirzepatide 可能導致症狀性低血壓,需調整合併用藥。 -
Arillotta D, et al. (2023). GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Related Mental Health Issues: A Comprehensive Review. Current Neuropharmacology.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑有觸發憂鬱、自殺傾向、行為等風險。 -
De Giorgi R, et al. (2025). An analysis on the role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders. Nature Mental Health.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑對情緒/焦慮障礙作用證據各異,利弊兼具。 -
Almeida OP, et al. (2024). Cross-sectional, case-control and longitudinal associations between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and antidepressant use. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
主要發現:GLP-1 受體促效劑暴露者較易被處方抗憂鬱藥。 -
Holt RIG, et al. (2019). Association Between Antipsychotic Medication Use and Diabetes. Current Diabetes Reports.
主要發現:抗精神病藥物因體重增加及胰島素敏感性下降導致糖尿病風險提升。